A community-based program was found to improve QOL for patients with varying levels of social vulnerability.
Disparities in Diabetes
Advertisement
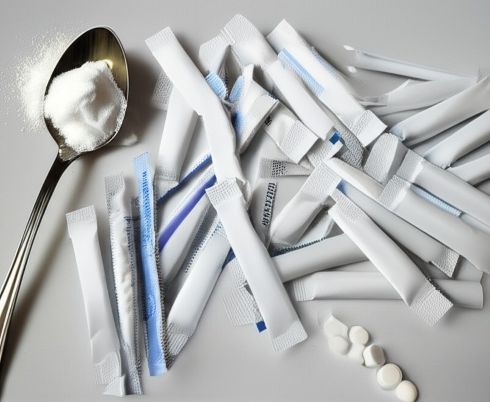
The findings suggest that approximately one-fifth of Americans who consume diet drinks may benefit from this substitution.
Panelists call on fellow healthcare practitioners to create progress in reducing disparities in T2D over the next decade.
The results support that circadian misalignment, rather than meal-to-sleep interval, underlies the adverse glucose effects.
Experts discuss strategies for system-level changes to improve multidisciplinary collaboration and improve diabetes outcomes.
Margaret Zupa, MD, and colleagues found that increased telehealth use since COVID-19 has not improved access to specialists.
The panel explores the impact of health disparities on heart and kidney complications of T2D.
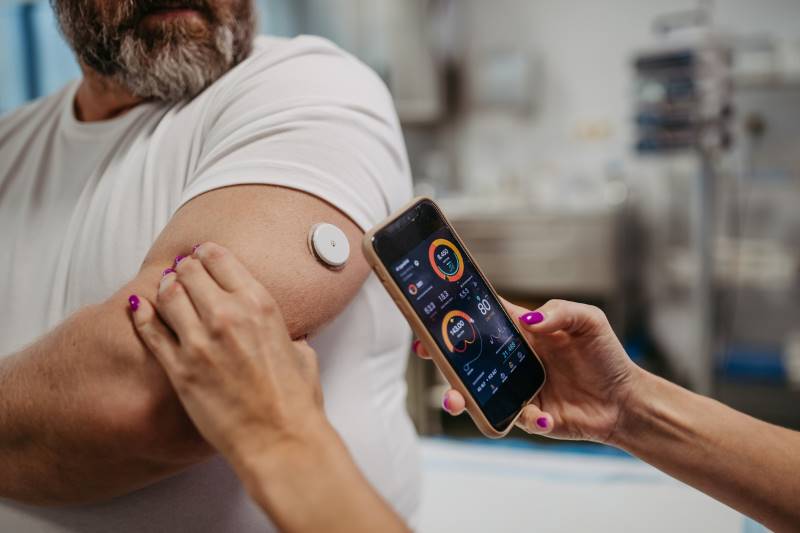
Black and Hispanic patients were less likely to initiate use of continuous glucose monitoring devices.
The study found that participants consuming the most diet beverages had more than double the diabetes risk.
Expert Interviews
Urban Health Today reports on clinical news and policy updates that directly impact urban health care providers and their patients.
Get research and expert insights straight to your inbox.








 © 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.
© 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.